Hot flash triggers, a prevalent concern during menopause, are multifaceted and can stem from various sources. Understanding these triggers is crucial for managing their frequency and severity, leading to improved quality of life. This comprehensive guide delves into the environmental, lifestyle, medical, and emotional factors that can provoke hot flashes, empowering individuals to take proactive measures for effective management.
Triggers Related to Environment
Environmental factors play a significant role in triggering hot flashes. Understanding these triggers can help women manage their symptoms more effectively.
Temperature
- Hot flashes are more likely to occur in warm or humid environments.
- Extreme heat can cause the body to overheat, leading to increased blood flow to the skin and a drop in blood pressure, which can trigger hot flashes.
Humidity
- High humidity can make it difficult for the body to cool down, leading to increased sweating and hot flashes.
- When the air is humid, sweat evaporates less efficiently, which can cause the body to overheat.
Altitude
- Hot flashes may be more frequent and severe at higher altitudes.
- At higher altitudes, the air is thinner, which means there is less oxygen available to the body.
- This can lead to increased heart rate and blood pressure, which can trigger hot flashes.
Air Pollution
- Exposure to air pollution, such as particulate matter and ozone, has been linked to increased hot flashes.
- Air pollution can irritate the respiratory system and cause inflammation, which can lead to hot flashes.
Seasonal Changes
- Hot flashes may be more frequent during certain seasons, such as summer or spring.
- During these seasons, the weather is often warmer and more humid, which can trigger hot flashes.
- Additionally, changes in daylight hours and hormone levels can also contribute to seasonal variations in hot flash frequency.
Triggers Related to Lifestyle
Lifestyle factors can significantly influence the frequency and intensity of hot flashes. Understanding the connection between certain behaviors and hot flashes can help individuals develop strategies to manage these symptoms effectively.
Caffeine and Alcohol Consumption
Caffeine and alcohol are both known to trigger hot flashes. Caffeine stimulates the nervous system, which can lead to increased body temperature and vasodilation (widening of blood vessels). Alcohol, on the other hand, dilates blood vessels, which can also contribute to hot flashes.
Smoking and Stress
Smoking and stress are both associated with increased hot flash frequency and intensity. Nicotine in cigarettes stimulates the release of stress hormones, which can trigger hot flashes. Stress, both physical and emotional, can also lead to the release of stress hormones, contributing to hot flashes.
Diet and Exercise
Diet and exercise can play a role in managing hot flashes. Eating a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help maintain a healthy weight and reduce inflammation, which may contribute to hot flashes. Regular exercise can also help reduce stress and improve overall well-being, which can have a positive impact on hot flash symptoms.
Triggers Related to Medications and Treatments

Medications and treatments can also trigger hot flashes. Certain medications, such as hormone replacement therapy (HRT), antidepressants, and chemotherapy drugs, are known to cause hot flashes as a side effect.
Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT)
HRT is a treatment option for women experiencing menopausal symptoms, including hot flashes. However, HRT itself can trigger hot flashes in some women, especially during the first few months of treatment.
Antidepressants
Certain antidepressants, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), can cause hot flashes as a side effect.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy drugs, used to treat cancer, can cause hot flashes as a side effect. This is because chemotherapy drugs can damage the ovaries, leading to a decrease in estrogen production and triggering hot flashes.
Medical Conditions and Surgical Procedures
Certain medical conditions and surgical procedures can also trigger hot flashes. These include:
- Thyroid problems
- Pituitary gland tumors
- Ovarian cancer
- Hysterectomy (surgical removal of the uterus)
Triggers Related to Emotional and Psychological Factors
Emotional and psychological factors can significantly influence the severity and frequency of hot flashes. Understanding the connection between these factors and hot flashes is crucial for effective management.
Anxiety and Hot Flashes
Anxiety is a common trigger for hot flashes. When a person experiences anxiety, their body releases hormones like adrenaline and cortisol, which can cause an increase in heart rate, blood pressure, and body temperature. This surge in body temperature can trigger a hot flash.
Mood Swings and Sleep Disturbances, Hot flash triggers
Mood swings and sleep disturbances are often associated with hot flashes. During menopause, fluctuating hormone levels can lead to mood swings, irritability, and difficulty sleeping. These factors can exacerbate hot flashes by increasing stress and anxiety levels.
Emotional Triggers and Stress Management
Certain emotional triggers, such as anger, frustration, or embarrassment, can also trigger hot flashes. Identifying and managing these triggers can help reduce the frequency and severity of hot flashes.
Stress management techniques, such as relaxation exercises, yoga, or meditation, can help reduce anxiety and improve sleep quality, thereby reducing the impact of hot flashes.
Closing Notes: Hot Flash Triggers
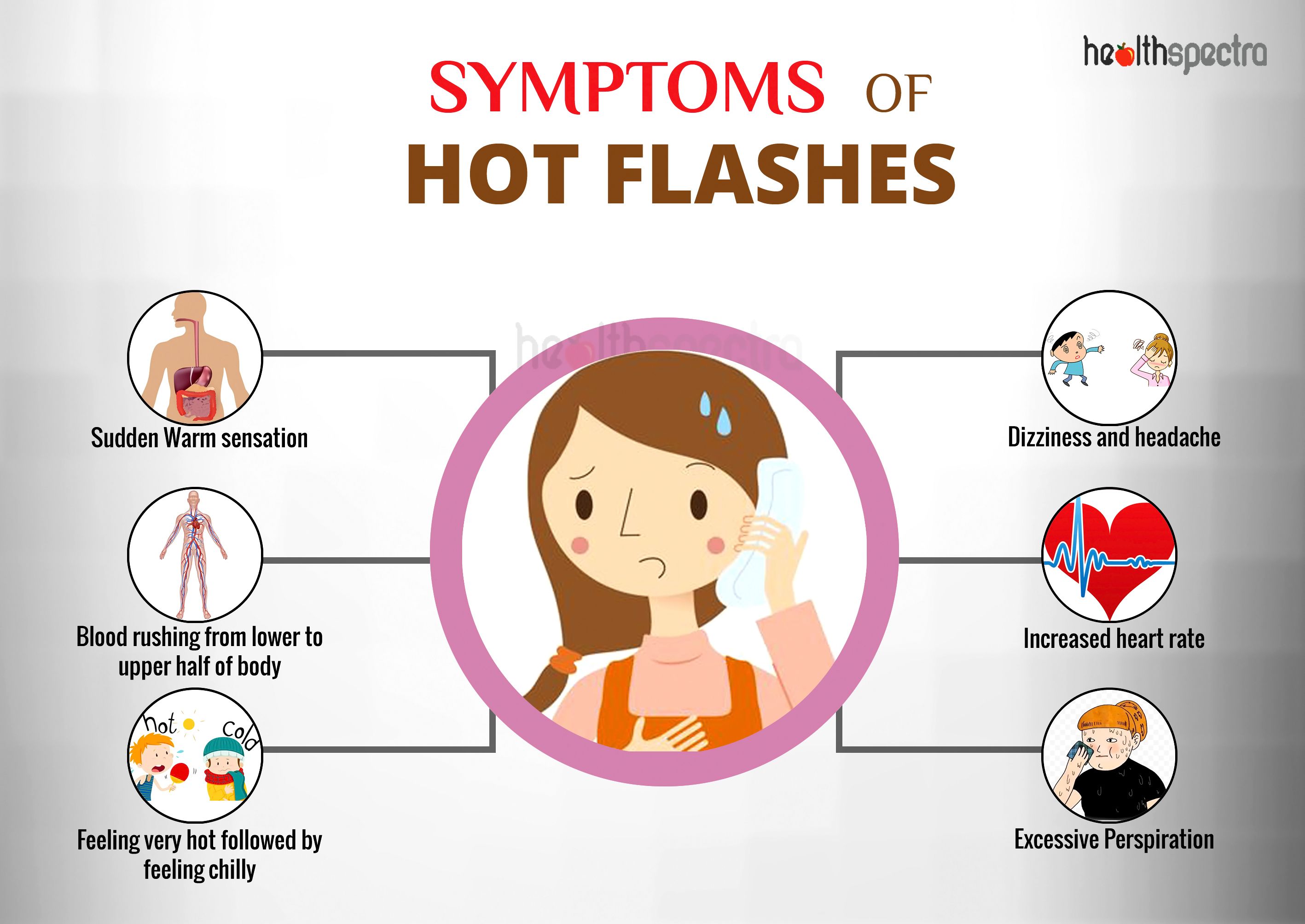
In conclusion, hot flash triggers are a complex interplay of environmental, lifestyle, medical, and emotional factors. By identifying and addressing these triggers, individuals can significantly reduce the frequency and intensity of hot flashes, enhancing their overall well-being during menopause. Remember, every individual’s experience is unique, and seeking personalized guidance from a healthcare professional is always advisable for optimal management strategies.
FAQ Corner
What are the most common environmental triggers for hot flashes?
Temperature fluctuations, humidity, and air pollution are common environmental triggers for hot flashes.
Can certain foods or drinks trigger hot flashes?
Yes, caffeine, alcohol, and spicy foods can act as triggers for hot flashes.
How does stress affect hot flashes?
Stress can increase the frequency and intensity of hot flashes.
Are there any medications that can trigger hot flashes?
Yes, certain medications, such as hormone replacement therapy and antidepressants, can cause hot flashes as a side effect.
What are some effective ways to manage hot flashes?
Lifestyle modifications, such as avoiding triggers, managing stress, and maintaining a healthy weight, can help reduce hot flash severity.