Severe hot flashes treatment – As severe hot flashes take center stage, this opening passage beckons readers into a world crafted with knowledge, ensuring a reading experience that is both absorbing and distinctly original.
Severe hot flashes are a common and often debilitating symptom of menopause, affecting millions of women worldwide. This article delves into the causes, risk factors, and treatment options for severe hot flashes, empowering individuals to manage their symptoms effectively.
Severe Hot Flashes

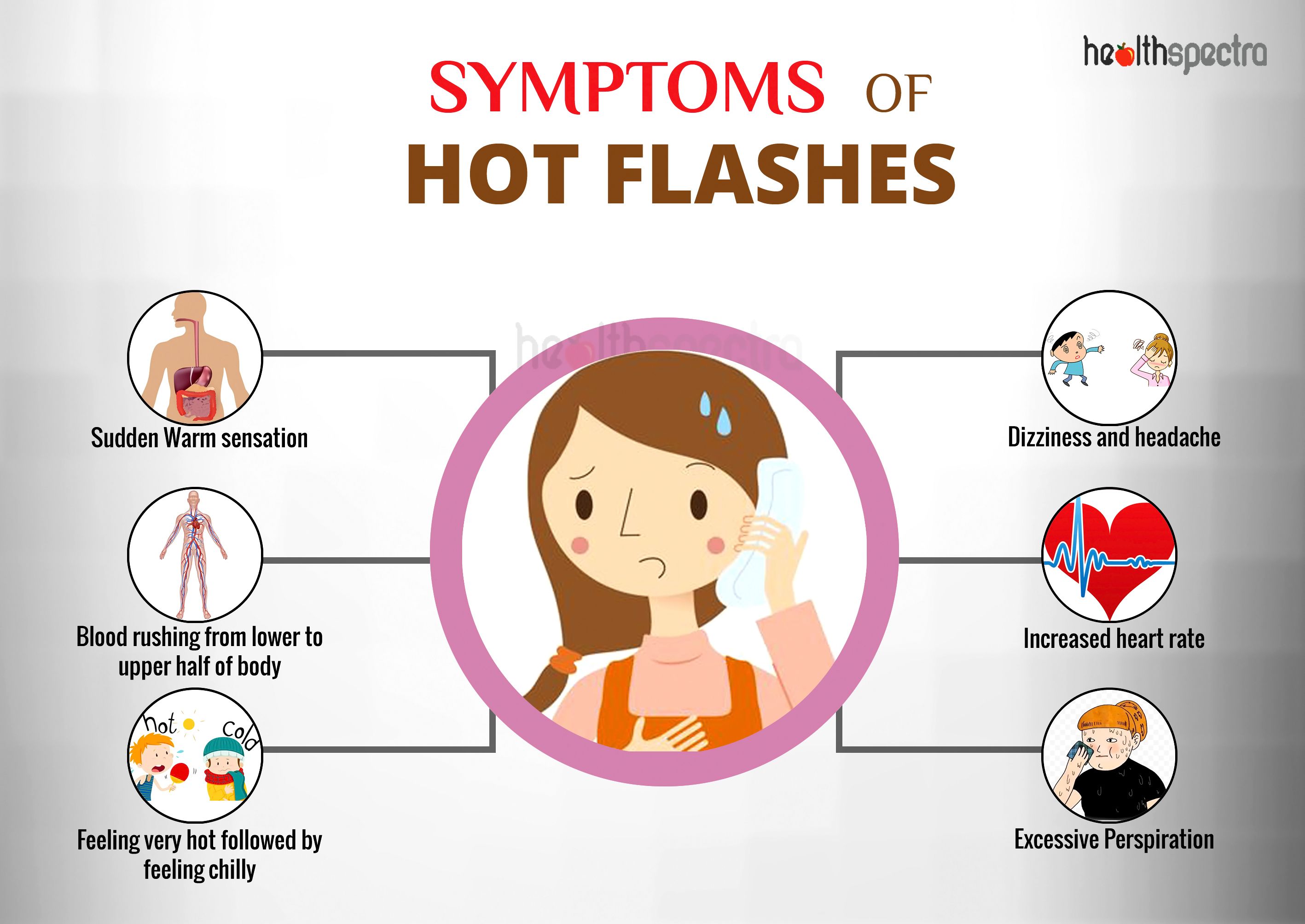
Severe hot flashes are intense, sudden sensations of heat that can cause significant discomfort and interfere with daily life. They are a common symptom of menopause, the transition when a woman’s menstrual periods stop.
Hot flashes can range in severity from mild to severe. Severe hot flashes are characterized by:
- Intense heat that spreads over the face, neck, and chest
- Profuse sweating
- Rapid heart rate
- Difficulty breathing
- Lightheadedness or dizziness
- Nausea or vomiting
Impact of Hot Flashes
Severe hot flashes can have a significant impact on physical and mental health. Physically, they can lead to:
- Sleep disturbances
- Fatigue
- Headaches
- Muscle aches
- Skin irritation
Mentally, severe hot flashes can cause:
- Anxiety
- Depression
- Irritability
- Difficulty concentrating
- Mood swings
Causes and Risk Factors: Severe Hot Flashes Treatment
Severe hot flashes are primarily caused by hormonal imbalances during menopause, when the ovaries reduce estrogen production. This decline triggers various physiological changes that can lead to the characteristic symptoms of hot flashes, including sudden feelings of intense heat, sweating, and rapid heart rate.
Risk Factors
Certain factors can increase the risk of experiencing severe hot flashes:
- Age:The risk of hot flashes increases with age, especially during the perimenopausal and menopausal years.
- Obesity:Excess body weight can contribute to hormonal imbalances and increase the severity of hot flashes.
- Smoking:Smoking cigarettes can interfere with estrogen production and worsen hot flashes.
- Family history:Women with a family history of hot flashes are more likely to experience them themselves.
li> Certain medical conditions:Conditions such as thyroid disorders, diabetes, and heart disease can affect hormone levels and increase the risk of hot flashes.
Treatment Options
Severe hot flashes can significantly impact a person’s quality of life. Fortunately, various treatment options are available to manage these symptoms.
The choice of treatment depends on the severity of hot flashes, underlying medical conditions, and individual preferences. It is crucial to consult a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate treatment plan.
Pharmacological Therapies
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT) | Hormonal | Replaces hormones lost during menopause, reducing hot flashes and other menopausal symptoms. |
| Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs) | Antidepressant | Inhibits serotonin reuptake in the brain, potentially reducing hot flash frequency and severity. |
| Serotonin-Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors (SNRIs) | Antidepressant | Similar to SSRIs, but also affects norepinephrine levels, which may provide additional benefits for hot flashes. |
| Gabapentin | Anticonvulsant | Originally used for seizures, but has shown effectiveness in reducing hot flashes by blocking certain nerve signals. |
| Clonidine | Antihypertensive | Lowers blood pressure and may also reduce hot flash severity by acting on the central nervous system. |
Note:All medications have potential side effects. It is important to discuss these with a healthcare professional before starting any treatment.
Non-Hormonal Therapies
Non-hormonal therapies offer alternative approaches to managing severe hot flashes without the use of hormone replacement therapy (HRT). These therapies focus on lifestyle modifications, behavioral interventions, and alternative treatments.
Lifestyle modifications include:
- Weight management:Maintaining a healthy weight can help reduce hot flashes.
- Dietary changes:Avoiding spicy foods, caffeine, and alcohol can trigger hot flashes.
- Regular exercise:Exercise can improve overall health and reduce hot flashes.
- Stress management:Techniques like yoga, meditation, and deep breathing can help manage stress, which can trigger hot flashes.
- Sleep hygiene:Establishing a regular sleep schedule and creating a relaxing bedtime routine can improve sleep quality and reduce hot flashes.
Behavioral interventions include:
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT):CBT helps individuals identify and change negative thoughts and behaviors that contribute to hot flashes.
- Hypnosis:Hypnosis can help reduce the severity and frequency of hot flashes.
- Biofeedback:Biofeedback teaches individuals to control their body’s responses, including hot flashes.
Alternative treatments include:
- Acupuncture:Acupuncture has been shown to reduce hot flashes in some women.
- Herbal remedies:Certain herbs, such as black cohosh and red clover, have been traditionally used to treat hot flashes.
- Supplements:Some supplements, such as vitamin E and isoflavones, may help reduce hot flashes.
Hormonal Therapies

Hormonal therapies are a common treatment option for severe hot flashes. These therapies work by replacing the hormones that are lost during menopause, which can help to reduce the frequency and severity of hot flashes.
There are two main types of hormonal therapies: estrogen-only therapy and estrogen-plus-progestin therapy. Estrogen-only therapy is typically used for women who have had a hysterectomy, while estrogen-plus-progestin therapy is used for women who still have their uterus.
The effectiveness of hormonal therapies varies depending on the individual woman. However, most women experience a significant reduction in hot flashes within a few weeks of starting treatment.
The following table summarizes the different types of hormonal therapies, their dosages, and their administration methods:
| Name | Type | Dosage | Administration Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Estrogen-only therapy | Estrogen | Varies | Oral, transdermal, or vaginal |
| Estrogen-plus-progestin therapy | Estrogen and progestin | Varies | Oral, transdermal, or vaginal |
Surgical Options
Surgical interventions may be considered for severe hot flashes that do not respond to other treatments. These procedures aim to reduce the production of estrogen or block its effects on the body.
Surgical options include:
- Oophorectomy (removal of ovaries):This procedure removes the ovaries, the primary source of estrogen production. It is a permanent solution and may also relieve other symptoms associated with menopause, such as irregular periods and pelvic pain.
- Hysterectomy (removal of uterus):This procedure removes the uterus and may also involve the removal of the ovaries. It is a permanent solution that can relieve hot flashes and other menopausal symptoms.
- Endometrial ablation:This procedure destroys the lining of the uterus, reducing estrogen production. It is a less invasive option than hysterectomy but may not be as effective in treating hot flashes.
Surgical options for severe hot flashes should be carefully considered and discussed with a healthcare professional. The risks and benefits of each procedure vary depending on individual circumstances.
Complementary and Alternative Therapies
In addition to conventional medical treatments, certain complementary and alternative therapies may provide relief from severe hot flashes. These therapies aim to address the underlying imbalances that contribute to hot flashes, offering a holistic approach to symptom management.
Some complementary and alternative therapies that may alleviate hot flashes include:
Acupuncture
- Acupuncture involves the insertion of thin needles into specific points on the body to stimulate energy flow and balance.
- Studies have shown that acupuncture may reduce the frequency and severity of hot flashes by regulating hormonal imbalances and improving circulation.
Herbal Remedies, Severe hot flashes treatment
- Certain herbs, such as black cohosh, red clover, and chasteberry, have been traditionally used to alleviate hot flashes.
- These herbs may contain compounds that mimic estrogen or help regulate hormone production, thereby reducing the intensity of hot flashes.
Dietary Supplements
- Dietary supplements like soy isoflavones, evening primrose oil, and vitamin E have shown some promise in reducing hot flashes.
- Soy isoflavones, which are plant-based compounds similar to estrogen, may help balance hormone levels and reduce hot flash severity.
Management Strategies
Coping with severe hot flashes can be challenging, but there are effective self-management strategies that can help reduce their intensity and frequency.
Self-management strategies focus on lifestyle modifications, stress reduction techniques, and cooling methods to mitigate the discomfort associated with hot flashes.
Cooling Techniques
- Wear loose, breathable clothing made from natural fibers like cotton or linen.
- Take cool showers or baths to lower body temperature.
- Use cooling towels or wraps around the neck, wrists, or ankles.
- Carry a portable fan or mister to cool down when needed.
- Drink plenty of cold fluids, such as water or herbal tea.
Stress Reduction
Stress can trigger hot flashes, so it’s important to find effective stress management techniques.
- Practice relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, yoga, or meditation.
- Engage in regular physical activity to reduce stress levels.
- Get enough sleep to promote overall well-being.
- Seek support from family, friends, or a therapist to manage stress.
Lifestyle Modifications
- Avoid caffeine and alcohol, as they can worsen hot flashes.
- Eat a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Maintain a healthy weight, as excess weight can contribute to hot flashes.
- Consider using herbal supplements such as black cohosh or red clover, which may help reduce hot flash severity.
- Avoid smoking, as nicotine can trigger hot flashes.
9. Research and Advancements
Research on severe hot flashes is ongoing, with promising advancements emerging. Clinical trials are evaluating new treatment options and exploring the underlying mechanisms of hot flashes.
Key research advancements include:
Emerging Treatment Options
- Targeted Therapies:Medications that block specific receptors or enzymes involved in hot flashes, such as neurokinin-1 antagonists and substance P antagonists.
- Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS):A non-invasive procedure that uses magnetic pulses to stimulate brain areas involved in temperature regulation.
- Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS):An implantable device that sends electrical pulses to the vagus nerve, which may help regulate body temperature.
Ongoing Clinical Trials
Numerous clinical trials are currently investigating the efficacy and safety of new treatments for severe hot flashes. These trials involve various treatment modalities, including medications, devices, and behavioral interventions.
Understanding the Mechanisms
Research is also focused on understanding the underlying mechanisms of hot flashes. This includes studying the role of hormones, neurotransmitters, and the autonomic nervous system in the development and severity of hot flashes.
Conclusion

In conclusion, severe hot flashes can significantly impact a woman’s quality of life. It is essential to seek professional medical advice to determine the underlying cause and explore the most appropriate treatment options.
Non-hormonal therapies, hormonal therapies, and surgical options provide a range of approaches to manage hot flashes. Complementary and alternative therapies can also offer additional support and symptom relief. It is important to work closely with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses individual needs and preferences.
Final Conclusion
In conclusion, severe hot flashes are a manageable condition with a wide range of treatment options available. By understanding the underlying causes, risk factors, and available therapies, individuals can make informed decisions and find relief from this common menopausal symptom.
It is crucial to seek professional medical advice to determine the most appropriate treatment plan based on individual needs and circumstances.
Helpful Answers
What are the most common causes of severe hot flashes?
The most common cause of severe hot flashes is the hormonal changes associated with menopause, particularly the decline in estrogen levels.
What are some non-hormonal treatment options for severe hot flashes?
Non-hormonal treatment options include lifestyle modifications such as avoiding triggers, managing stress, and using cooling techniques. Medications like antidepressants and anticonvulsants can also be effective.
When should I seek professional medical advice for severe hot flashes?
It is important to seek professional medical advice if severe hot flashes significantly impact your daily life, interfere with sleep, or cause other health concerns.