What is hot flash? It’s a common symptom experienced by many individuals, often associated with hormonal changes. This guide delves into the definition, causes, impact, management, and unique experiences of hot flashes, providing a comprehensive understanding of this condition.
Hot flashes can significantly impact individuals’ physical, emotional, and social well-being. This guide explores the physiological mechanisms underlying hot flashes and discusses evidence-based strategies for managing their frequency and severity.
Definition of Hot Flashes
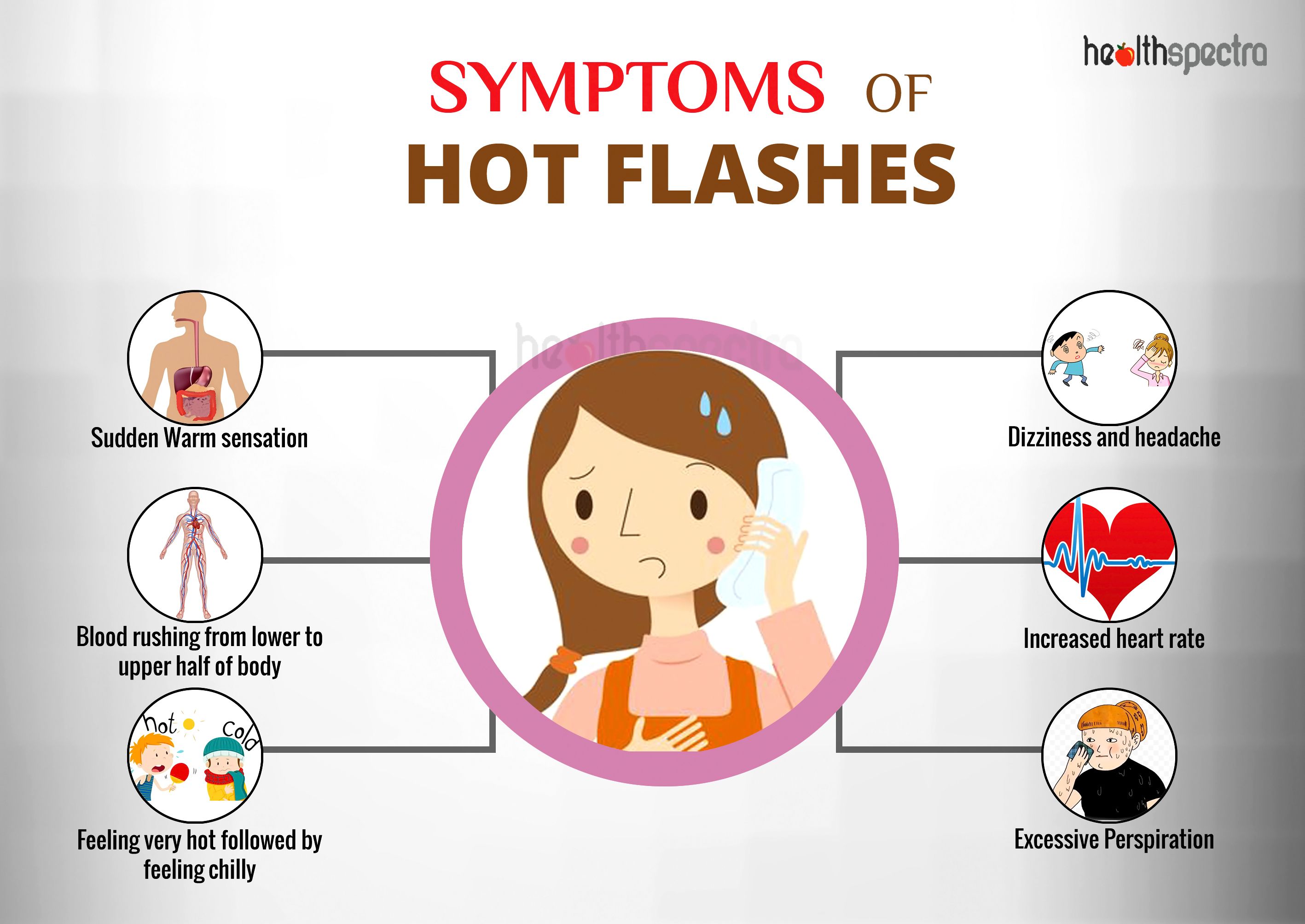
Hot flashes are a common symptom of menopause, characterized by a sudden feeling of intense heat that spreads over the body, often accompanied by sweating and flushing of the face, neck, and chest. These episodes can last anywhere from a few seconds to several minutes and occur several times a day or night.
Triggers
The exact cause of hot flashes is unknown, but they are thought to be related to changes in hormone levels, particularly estrogen, during menopause. Other factors that can trigger hot flashes include:
- Spicy foods
- Caffeine
- Alcohol
- Stress
- Smoking
Causes of Hot Flashes
Hot flashes are primarily caused by hormonal changes associated with menopause, particularly the decline in estrogen levels. Estrogen plays a crucial role in regulating body temperature by influencing the hypothalamus, the brain’s temperature control center. As estrogen levels drop during menopause, the hypothalamus becomes more sensitive to slight increases in body temperature, triggering a cascade of physiological responses that result in a hot flash.
During a hot flash, the blood vessels in the skin dilate, increasing blood flow to the skin’s surface. This causes the skin to feel warm and flushed. The body also sweats in an attempt to cool down, leading to the characteristic perspiration associated with hot flashes.
Other Contributing Factors
In addition to hormonal changes, several other factors can contribute to the frequency and severity of hot flashes, including:
- Certain medications, such as chemotherapy drugs and antidepressants
- Alcohol consumption
- Smoking
- Caffeine intake
- Spicy foods
- Stress and anxiety
Impact of Hot Flashes
Hot flashes can significantly impact individuals’ physical, emotional, and social well-being. These sudden and intense sensations of heat can disrupt daily activities, impair sleep, and affect overall quality of life.
The physical effects of hot flashes include:
- Sudden feeling of intense heat in the face, neck, and chest
- Profuse sweating
- Rapid heartbeat
- Flushing or redness of the skin
- Chills or shivering after the hot flash subsides
The emotional impact of hot flashes can be equally distressing:
- Anxiety and irritability
- Difficulty concentrating
- Mood swings
- Feeling overwhelmed or embarrassed
- Disrupted sleep
Hot flashes can also have a negative impact on social interactions:
- Avoiding social situations due to fear of experiencing a hot flash
- Feeling self-conscious or uncomfortable in public
- Difficulty engaging in physical activities or hobbies due to fear of sweating or overheating
- Relationship problems due to irritability or disrupted sleep
| Symptom | Effect |
|---|---|
| Sudden heat | Discomfort, sweating |
| Profuse sweating | Embarrassment, discomfort |
| Rapid heartbeat | Anxiety, discomfort |
| Flushing | Self-consciousness, embarrassment |
| Chills | Discomfort, disruption of sleep |
| Anxiety | Emotional distress, difficulty concentrating |
| Irritability | Relationship problems, social withdrawal |
| Mood swings | Emotional instability, difficulty managing relationships |
| Disrupted sleep | Fatigue, difficulty concentrating |
| Social withdrawal | Isolation, loneliness |
Management of Hot Flashes

Hot flashes can be managed through a combination of lifestyle modifications, medications, and alternative therapies. The goal of management is to reduce the frequency and severity of hot flashes and improve overall quality of life.
Lifestyle modifications that may help manage hot flashes include:
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Avoiding triggers such as caffeine, alcohol, and spicy foods
- Dressing in layers to facilitate temperature regulation
- Using cooling techniques such as fans or cold compresses
- Engaging in regular exercise
- Getting enough sleep
- Managing stress
Medications that may be used to treat hot flashes include:
- Hormone replacement therapy (HRT)
- Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs)
- Venlafaxine
- Gabapentin
Alternative therapies that may provide some relief from hot flashes include:
- Acupuncture
- Yoga
- Meditation
- Herbal remedies such as black cohosh and red clover
It is important to note that the effectiveness of these management strategies may vary from person to person. It is recommended to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate approach for individual needs.
Differential Diagnosis of Hot Flashes
Hot flashes are a common symptom of menopause, but they can also be caused by other conditions. It is important to differentiate between hot flashes and other conditions to ensure proper diagnosis and treatment.
Conditions with Similar Symptoms
- Anxiety disorders:Anxiety can trigger symptoms similar to hot flashes, such as sweating, heart palpitations, and shortness of breath.
- Thyroid disorders:An overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism) can cause hot flashes, sweating, and weight loss.
- Medications:Certain medications, such as antidepressants and steroids, can cause hot flashes as a side effect.
- Infections:Some infections, such as tuberculosis and HIV, can cause fever and sweating, which may resemble hot flashes.
- Pheochromocytoma:A rare tumor of the adrenal glands can cause episodes of sweating, heart palpitations, and high blood pressure that may be mistaken for hot flashes.
| Symptom | Hot Flashes | Other Conditions |
|---|---|---|
| Onset | Sudden | Gradual or sudden |
| Duration | A few minutes | Minutes to hours |
| Frequency | Varies | Varies |
| Triggers | Hormonal changes, spicy foods, caffeine | Stress, heat, exercise, certain foods |
| Associated symptoms | Facial flushing, sweating, heart palpitations | Anxiety, nervousness, weight loss, fever |
Hot Flashes in Specific Populations
Hot flashes can affect individuals of different ages, genders, and health conditions. Specific populations may experience unique challenges and require tailored management strategies.
Transgender Individuals
Transgender individuals who are taking hormone therapy may experience hot flashes as a side effect. These hot flashes can be particularly challenging for those who are transitioning from female to male, as they may already be experiencing hormonal changes associated with testosterone therapy.
- Management:
- Consider reducing the dosage or frequency of testosterone therapy.
- Explore alternative hormone therapies, such as estradiol or progesterone.
- Utilize cooling measures, such as cold showers, ice packs, or fans.
Cancer Survivors
Cancer survivors who have undergone certain treatments, such as chemotherapy or radiation therapy, may experience hot flashes as a side effect. These hot flashes can be particularly severe and persistent.
- Management:
- Consider hormone replacement therapy (HRT) to regulate hormonal imbalances.
- Explore complementary therapies, such as acupuncture, yoga, or mindfulness-based stress reduction.
- Utilize non-hormonal medications, such as gabapentin or clonidine, to reduce hot flash severity.
Older Adults, What is hot flash
Older adults, particularly postmenopausal women, are more likely to experience hot flashes. These hot flashes can be associated with hormonal changes and can have a significant impact on quality of life.
- Management:
- Consider HRT to alleviate hot flash symptoms.
- Explore lifestyle modifications, such as regular exercise, stress management, and dietary changes.
- Utilize over-the-counter cooling products, such as cooling sprays or wipes.
Future Research on Hot Flashes: What Is Hot Flash
Research on hot flashes is ongoing, with a focus on developing new treatments and exploring the underlying mechanisms that trigger them. Future research directions include:
Identification of Risk Factors
Identifying risk factors for hot flashes can help predict who is more likely to experience them and develop targeted prevention strategies.
Development of New Treatments
Current treatments for hot flashes are not always effective or well-tolerated. Research is ongoing to develop new treatments that are more effective, have fewer side effects, and target specific mechanisms that contribute to hot flashes.
Exploration of Underlying Mechanisms
Understanding the mechanisms that trigger hot flashes can lead to the development of more effective treatments. Research is ongoing to investigate the role of hormones, the nervous system, and other factors in hot flashes.
Research Questions
Some specific research questions that need to be addressed to further understand and manage hot flashes include:
- What are the most effective treatments for hot flashes in different populations?
- What are the long-term effects of hot flashes on health and well-being?
- Can hot flashes be prevented or delayed?
- What are the underlying mechanisms that trigger hot flashes?
- How can we improve the quality of life for people who experience hot flashes?
Conclusive Thoughts

Hot flashes are a complex and multifaceted experience. By understanding their causes, impact, and management strategies, individuals can navigate this condition effectively. Ongoing research continues to shed light on hot flashes, promising advancements in treatment and prevention.
Helpful Answers
What are the common triggers of hot flashes?
Hot flashes can be triggered by various factors, including hormonal fluctuations, spicy foods, caffeine, alcohol, stress, and certain medications.
How can I manage hot flashes naturally?
Lifestyle modifications such as regular exercise, stress management techniques, and dietary changes (e.g., reducing caffeine and alcohol intake) can help manage hot flashes.
When should I seek medical attention for hot flashes?
If hot flashes are severe, persistent, or interfere with daily life, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional to rule out any underlying medical conditions.